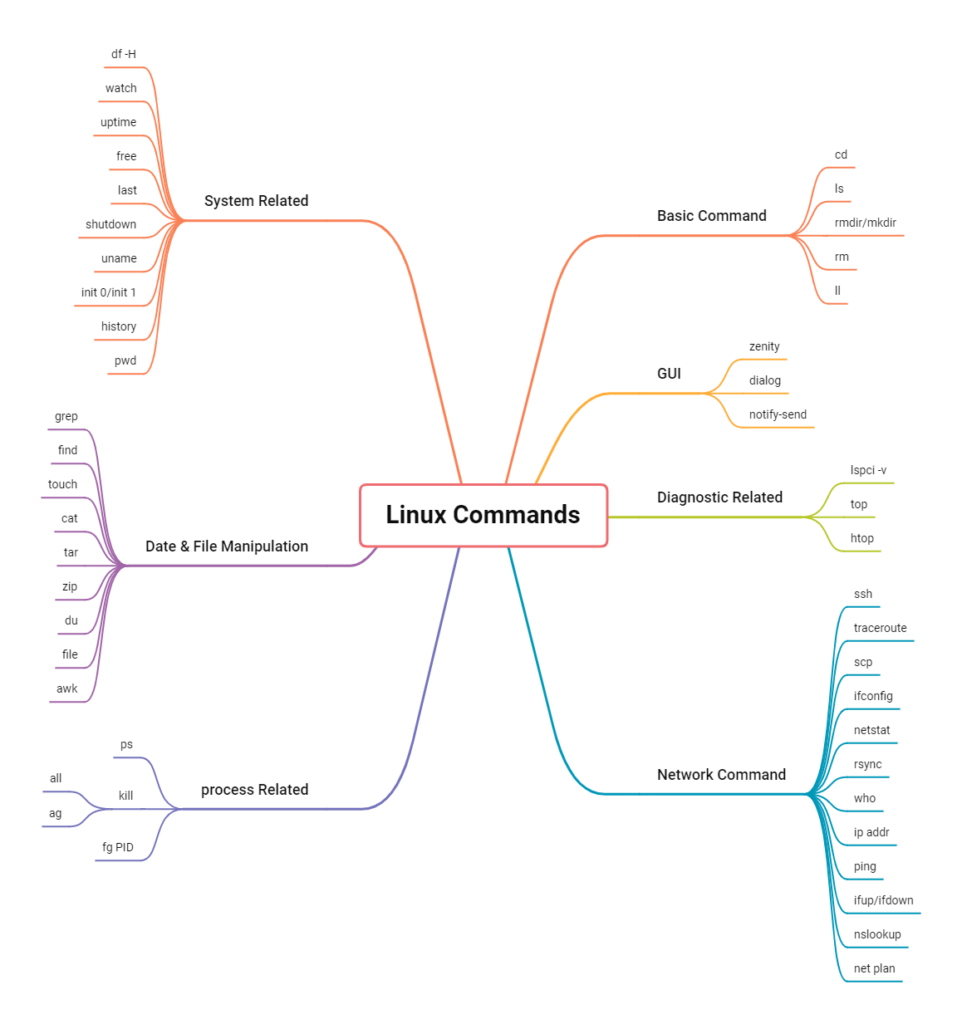
In this tutorial, we are learning about all the essential basic Linux commands for beginners. Here is a list of all the commands.
- apropos: Search through the Help manual pages
- apt-get: Install and search for software packages
- aspell: Spell checker
- awk: It lets you find text and replace it
- basename: Strips suffixes off files and directories
- bash: GNU Bourne-Again Shell
- bc: Arbitrary precision calculator language
- bg: Sends to the background
- break: Exit from a loop
- builtin: Run a shell builtin
- bzip2: Compresses or decompresses files
- cal: Displays calendar
- case: Perform a command conditionally
- cat: Displays the content of the files after concatenation
- cd: Change Directory
- cfdisk: Partition table manipulator
- chgrp: Changes the ownership of a group
- chmod: Changes the access permissions
- chown: Changes the owner and group of a file
- chroot: Run command, but with a different root directory
- cksum: It displays the CRC checksum ad byte counts
- clear: Clears the terminal screen
- cmp: Compares two files
- comm: Compares two sorted files line by line
- continue: Resumes the next iteration of a particular loop
- cp: Makes a copy of files to a different location
- cron: Executes scheduled Linux commands
- crontab: Schedules a command that will run at a specified time
- csplit: Splits a file into context-determined pieces
- date: Changes the date and time
- dc: Desk Calculator
- ddrescue: Disk recovery tool
- declare: Declares the variables and gives attributes
- df: Gives the free space on your disk
- diff: Prints the differences between two files
- dig: Looks up the DNS
- dir: Lists directory contents briefly
- dirname: Changes a full pathname into just a path
- dirs: Shows you the list of directories that are remembered
- du: Get an estimation of the file space usage
- echo: Displays message on the screen
- egrep: Searches for files that have lines matching an extended expression
- enable: Disable/enable bulletin shell linux commands
- ethtool: Ethernet card settings
- eval: Evaluates many commands
- exec: Executes a command
- exit: Exiting the shell
- expand: Converts all the tabs to spaces
- export: Sets an environment variable
- expr: Evaluates expressions
- false: Do nothing, unsuccessfully
- fdformat: Perform low level format of a floppy disk
- fdisk: Partition table manipulator for Linux systems
- fg: Sends a task to the foreground
- fgrep: Searches through files for tasks that match a string
- file: Determines the file type
- find: Find files that match a desired criteria
- fmt: Reformats paragraph text
- fold: Wraps text in order to fit a certain width
- format: Formats tapes/disks
- free: Reveals the memory usage
- fsck: Checks the consistency of the file system and repairs it
- fuser: Identifies and kills the process accessing a file
- gawk: Finds text within files and replaces it
- getopts: Parse positional parameters
- grep: Searches in files for lines matching a certain pattern
- groupadd: Adds security user groups
- groupdel: Deletes a certain group
- groupmod: Modifies a group
- groups: Prints the names of groups in which a user is located
- gzip: Compresses/decompresses files
- hash: Complete pathname of a name argument
- head: Outputs the first part of files
- history: Command History
- hostname: Print/set system name
- iconv: Converts the character set in files
- id: Displays the group ids/user ids
- if: Conditional command
- ifconfig: Configures network interfaces using ifconfig
- ifdown: Stops a network interface
- ifup: Starts a network interface app
- import: Captures a screen and saves image in X server
- Install: Sets attributes and copies files
- jobs: Lists jobs that are active
- Join: Joins lines on a common field
- kill: Stops a process from running
- Killall: Kills processes by name
- less: Displays the output on a single screen at a time
- let: Performs arithmetic on shell variables
- link: Creates a link to another file
- ln: Creates a symbolic link to another file
- local: Creates variables
- locate: Finds files
- logname: Print the login name being used currently
- logout: Use this command to exit a login shell.
- lpc: Line Printer Control
- ls: List information about the files (the current directory by default)
- lpr: Offline print
- lprint: Prints a file
- lprintd: Aborts an ongoing print job
- lprintq: Lists the print queue
- lprm: Removes the jobs from the print queue
- make: Recompiles the group of programs
- man: Provides help on a command
- mkdir: Creates directories
- mkfifo: Makes FIFOs
- mknod: Creates character special files or block files
- more: Displays the output in a single screen at a time
- mount: Mounts a particular filesystem
- mtools: Manipulates files from MS-DOS
- mtr: Network diagnostics command
- mv: Moves and renames files and directories
- mmv: Mass Move and Rename
- netstat: Provides information on networking
- nice: Sets the priority of a job or a command
- nl: Writes files and number lines
- nohup: Runs a command not affected by hangups
- notify-send: Sends desktop notifications
- nslookup: Queries internet name servers interactively
- open: Opens a file in its default application
- op: Provides operator access
- passwd: Modifies user passwords
- paste: Merges lines in files
- pathchk: Checks the portability of a file name
- ping: Tests network connections
- pkill: Stops processes from running
- popd: Restores the previous value of the directory you’re currently in
- pr: Prepares your files for printing
- printcap: Printer capability database
- printenv: Print environment variables
- printf: Formats and prints data
- ps: Process Status
- pushd: Changes the directory and saves it first
- pwd: Print Working Directory
- quota: Displays the disk usage and its limits
- quotacheck: Lets you scan a file system to find its disk usage
- quotactl: Sets disk quotas
- ram: Ram disk device
- rcp: Copies files between two devices.
- read: Reads a line from standard input
- readarray: Reads from stdin into an array variable
- readonly: Marks the variables and functions as readonly
- reboot: Reboots your system
- rename: Renames files
- renice: Alters the priority of the processes running
- remsync: Synchronises remote files through email
- rev: Reverses the lines in a file
- rm: Removes particular files
- rsync: Synchronises file trees
- screen: Run remote shells using ssh
- scp: Creates a secure copy
- sdiff: Merges two files in a secure manner
- sed: Stream editor
- select: Accepts keyboard inputs
- seq: Prints numeric sequences
- set: Manipulates shell functions and variables
- sftp: Runs the secure file transfer program
- shift: Shifts positional parameters
- shopt: Shell Options
- shutdown: Shuts down Linux or restarts it
- sleep: Adds a delay
- slocate: Finds particular files
- sort: Sorts text files
- source: Runs commands from a file
- split: Breaks a file into fixed sizes
- ssh: Runs the remote login program
- strace: Traces signals and system calls
- su: Substitutes the user identity
- sudo: Executes commands as a different user
- suspend: Suspends the execution of the current shell
- sync: Synchronises data from a disk with the memory
- tail: Outputs only the last part of a file
- tar: Stores a list or extracts files in an archive
- tee: Redirects output into multiple files
- test: Evaluates conditional expressions
- time: Measures the running time of a program
- timeout: Puts a time limit on a command
- times: Finds the user and system times
- touch: Changes timestamps on a file
- traceroute: Trace Route to a host
- tr: Deletes characters, translates or squeezes them
- tsort: Topological sorting
- ulimit: Limits the user resources
- umask: Determines the file permission for a new file
- umount: Unmounts a device from the system
- unalias: Removes an alias
- uname: Prints the system information
- unexpand: Converts the spaces in a file to tabs
- uniq: Uniquify your files
- units: Converts the units from one scale to another
- unset: Removes the variable names or the function names
- unshar: Unpacks the shell archive scripts
- until: Executes a command until there is an error
- uptime: Shows the uptime
- usermod: Modifies a user account
- users: Gives you a list of users who are currently logged in
- uuencode: Encodes binary files
- v: Lists the contents of a directory
- vi: Text editor
- vmstat: Reports on the virtual memory statistics
- wait: Directs the system to wait for a process to finish
- watch: Displays or executes a program periodically
- wc: Prints the word, byte and line counts
- while: Executes commands
- who: Prints the usernames that are currently logged into the system
- whoami: Prints the current name and user id
- wget: Retrieves the web pages or files through HTTP, HTTPS or FTP
- write: Sends messages to other users
- xargs: Executes a utility and passes a constructed argument list
- xdg-open: Opens a URL or a file in the user’s preferred application
If you have any questions please leave them in the comments below.
